자바 입출력과 스트림
스트림이란?
- 자바에서 모든 입출력은 Stream을 통해 이루어진다. 파일 디스크 키보드 모니터 메모리 네트워크 등등 모두 포함.
- Stream이란 용어는 네트워크에서 유래됐다.
- 입출력장치가 다양하기 때문에 자바는 입출력 장치와 무관하고 일관성 있게 프로그램을 구현할 수 있도록 일종의 가상 통로인 Stream을 제송한다.
- Source와 target에 따라 각각 다른 Stream 클래스를 제공한다.
입력 스트림과 출력 스트림
- 입력 스트림 : 어떤 대상으로부터 자료를 읽어들일때 사용하는 스트림을 입력 스트림이라고 한다.
- 출력 스트림 : 파일에 저장할 때는 출력 스트림을 사용한다.
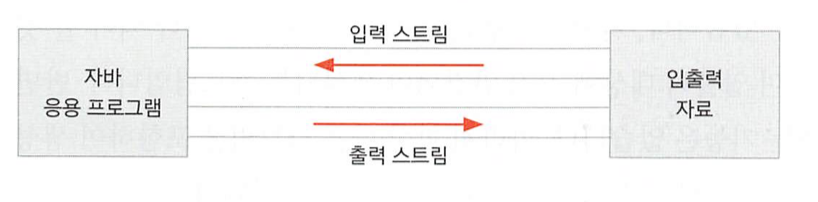
- 스트림은 단방향이다. 입력과 출력을 동시에 할 수 없다.
- 스트림의 이름을 보면 입력인지 출력인지 알 수 있다.
- 입력 스트림의 예
- FileInputStream, FileReader, BufferedInputStream, BufferedReader
- 출력 스트림의 예
- FileOutputStream, FileWriter, BufferedOutputStream, BufferedWriter
바이트 단위 스트림과 문자 스트림
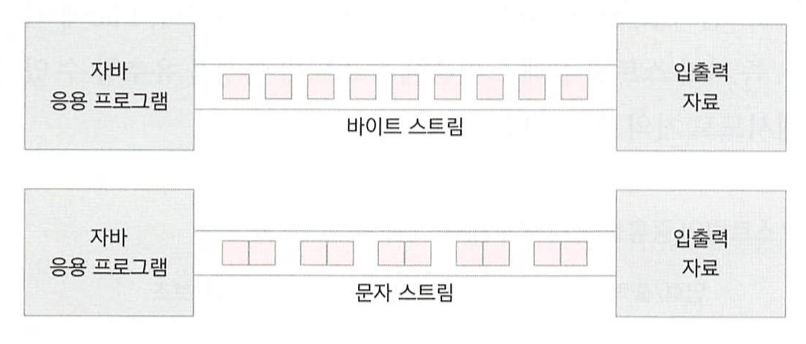
- 원래 자바의 스트림 단위는 바이트다.
- 그런데 char형은 2바이트라 1바이트만 읽으면 특수문자는 깨진다.
- 그래서 문자를 위한 스트림은 별도로 있다.
- 바이트 스트림의 예
- FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutputStream
- 문자 스트림의 예
- FileReader, FileWriter, BufferedReader, BufferedWriter
기반 스트림과 보조 스트림
- 기반 스트림 : 어떤 스트림이 자료를 직접 읽거나 쓰는 기능을 제공하는 스트림
- 보조 스트림 : 직접 읽고 쓰는 기능은 없고 다른 스트림에 부가기능을 제공하는 스트림
- 기반 스트림의 예
- FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader, FileWriter
- 보조 스트림의 예
- InputStreamReader, OutputStreamWriter, BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutputStream
- 이름만으로 기억하기는 어렵고 많이 사용하는 스트림 위주로 기억하자.
표준 입출력
- 화면에 출력하고 입력받는 표준 입출력 클래스
- static이기 때문에 인스턴스를 생성할 필요가 없다.
System.out은 표준 출력을 위한 객체다.- System class의 변수
static PrintStream out : 표준 출력 스트림static InputStream int : 표준 입력 스트림static OutputStream err : 표준 오류 출력 스트림
– PrintStream 은 OutputStream의 하위 클래스다.
System.in
Scanner
- Scanner는
java.util 패키지에 있는 입력 클래스다. - Scanner 클래스는 문자 뿐만 아니라 정수 실수 등 다른 자료형도 읽을 수 있다.
- Scanner class의 생성자
Scanner(File source) : 파일을 매개변수로 받아 Scanner를 생성한다.Scanner(InputStream source) : 바이트 스트림을 매개변수로 받아 Scanner를 생성한다.Scanner(String source) : String을 매개변수로 받아 Scanner를 생성한다.
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in)은 문자열을 입력하기 위해 자주 쓰는 방법이다. – 코드 보기- Scanner class의 메소드
boolean nextBoolean(), byte nextByte(), short nextShort(), int nextInt(), long nextLong(), float nextFloaf(), double nextDouble(), String nextLine()
Console
바이트 단위 스트림
- 입출력 기능을 구현하는데 기본으로 알아야 하는 클래스와 메소드. (바이트 스트림, 문자 스트림, 보조 스트림)
- 바이트 단위로 읽는 스트림 중 최상위 스트림.
- 추상 클래스로 각 하위 스트림 클래스가 상속받아 사용한다.
- 주로 사용되는 클래스들
FileInputStream : 파일에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 읽는다.ByteArrayInputStream : Byte배열 메모리에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 읽는다.FilterInputStream : 기반 스트림에서 자료를 읽을때 추가 기능을 제공하는 보조스트림.
- InputStream의 메소드
int read() : 읽은 바이트의 수를 반환int read(byte b[]) : 배열의 읽은 바이트 수를 반환int read(byte b[], int off, int len) : offset부터 length만큼 읽고 바이트 수를 반환void close() : 리소스 닫기
- 파일에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 읽어들일때 사용하는 스트림 클래스
- FileInputStream의 생성자
FileInputStream(String name) : 파일 이름을 매개변수로 받아 입력 스트림을 생성.FileInputStream(File f) : File 클래스를 메시지로 받아 입력 스트림을 생성.
파일에서 자료 읽기
파일 끝까지 읽기
public class FileInputStreamTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt")) {
int i;
while ((i = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) i);
}
System.out.println("end");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
fis.read()에서 -1이 반환되면 더이상 읽을 바이트가 없다는 뜻이다.
int read(byte[] b)
- 코드 보기
- 아래는 input2.txt에 해당하는 내용이다.
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
public class FileInputStreamTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input2.txt")) {
byte[] bs = new byte[10];
int i;
while ((i = fis.read(bs)) != -1) {
for (byte b : bs) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
System.out.println(": " + i + " 바이트 읽음.");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
ABCDEFGHIJ: 10 바이트 읽음.
KLMNOPQRST: 10 바이트 읽음.
UVWXYZQRST: 6 바이트 읽음.
end
- 마지막 6바이트에 QRST가 남아있는것은
for (byte b : bs)로 전체 순회를 했기 때문이다. - 그래서 bs를 순회하는 것이 아니라 읽는 바이트 수대로만 순회하면 된다.
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
System.out.print((char) bs[k]);
}
OutputStream
- 바이트 단위로 쓰는 스트림 중 최상위 스트림이다.
- OutputStream 하위 클래스
FileOutputStream : 바이트 단위로 파일에 자료를 쓴다.ByteArrayOutputStream : Byte배열에 바이트 단위로 자료를 쓴다.FilterOutputStream : 보조 스트림.
- OutputStream 메소드
void writer(int b) : 한 바이트를 출력한다.void write(byte[] b : 배열에 있는 자료를 출력한다.void write(byte b[], int off, int len) : 배열에 있는 자료의 offset위치 부터 length만큼 자료를 출력한다.void flush() : 출력을 위해 출력 버퍼를 비운다.void close() : 리소스 닫기. 출력 버퍼가 비워진다.
FileOutputStream
- 파일에 바이트 단위 자료를 출력하기 위해 사용하는 스트림이다.
- FileOutputStream 생성자
FileOutputStream(String name) : name파일에 대한 출력 스트림 생성FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) : append값이 true면 파일 스트림을 닫고 다시 생성할때 파일의 끝에 이어서 작성한다.FileOutputStream(File f,) : File클래스 출력스트림 생성FileOutputStream(File f, boolean append)
- 해당 경로에 파일이 없으면 파일을 새로 생성한다.
- 처음부터 덮어쓸지 기존에서 이어쓸지 결정할 수 있다. (append)
write()
write(byte[] b)
public class FileOutputStreamTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt", true);
try (fos) {
byte[] bs = new byte[26];
byte data = 65;
for (int i = 0; i < bs.length; i++) {
bs[i] = data;
data++;
}
fos.write(bs);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
fos.write(bs) : 배열을 쓰기한다.
flush(), close()
- 출력 스트림에서 flsuh()메소드의 기능은 강제로 자료를 출력하는 것이다. write()를 값을 썼다고 해도 바로 파일이나 네트워크로 전송되지 않고 출력을 위한 자료가 쌓이는 출력 버퍼에 어느정도 자료가 모여야 출력된다.
- 따라서 자료의 양이 출력할 만큼 많지 않으면 write()로 출력 했어도 파일에 쓰이지 않거나 전송되지 않을 수 있다.
- 이런 경우 flush()를 호출해야 한다.
- close()는 안에서 flush()를 호출해 버퍼가 비워지면서 남은 자료가 모두 출력된다.
문자 단위 스트림
Reader
- 문자 단위로 읽는 스트림 중 퇴상위 스트림으로 다음 하위 클래스를 주로 사용한다
- FileReader : 파일에서 문자 단위로 읽는 스트림 클래스
- InputStreamReader : 바이트 단위로 읽은 자료를 문자로 변환해주는 보조 스트림 클래스
- BufferedReader : 문자로 읽을 때 배열을 제공하여 한꺼번에 읽을 수 있는 기능을 제공해 주는 보조 스트림
- 아래와 같은 메소드를 제공한다
int read()int read(char[] buf)int read(char[], int off, int len)void close()
FileReader
- 생성자
FileReader(String name) : 파일 이름을 매개변수로 받아 입력 스트림을 생성한다.FileReader(File f) : File 클래스 정보를 매개변수로 받아 입력 스트림을 생성한다
- 한글 같은 2바이트 단위 문자들은 1바이트 단위로 읽어오면 깨진다. 따라서 문자를 입출력할때 문자 스트림을 사용해야 한다.
- 예제코드
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("reader.txt"); // 미리 만들어야한다.
try (fr) {
int i;
while ((i = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Writer
- 문자 단위로 출력하는 스트림 중 최상위 스트림으로 다음 하위 클래스가 있다
- FileWriter : 파일에 문자 단위로 출력하는 스트림 클래스다
- OutputStreamWriter : 파일에 바이트 단위로 출력한 자료를 문자로 변환해주는 보조 스트림이다
- BufferedWriter : 문자로 쓸 때 배열을 제공하여 한꺼번에 쓸 수 있는 기능을 제공하는 보조 스트림이다.
- 다음과 같은 메소드를 제공한다
void write(int c)void write(char[] buf)void write(char[] buf, int off, int len)void write(String str)void write(String str, int off, int len)void flush()void close()
FileWriter
- 다른 스트림 클래스와 마찬가지로 생성자를 사용해서 스트림을 생성한다.
- FileOutputStream 과 마찬가지로 출력파일이 없으면 생성한다.
- 생성자
FileWriter(String name)FileWriter(String name, boolean append)FileWriter(File f, )FileWriter(File f, boolean append)
- 예제 코드
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("writer.txt");
try (fw) {
fw.write('강');
char buf[] = {'H', 'E', 'L', 'L', 'O'};
fw.write(buf);
fw.write("안녕하세요");
fw.write("65");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
보조 스트림
- 스트림에 보조기능을 추가하는 보조 스트림.
- Wrapper 스트림이라고도 함.
- 스스로는 입출력 기능이 없다. 생성자의 매개변수로 다른 스트림을 받으면 자신이 감싸고 있는 스트림이 읽거나 기능을 수행할 때 기능을 추가한다.
- 데코레이터 패턴의 유명한 예.
- 보조스트림의 상위 클래스다. 모든 보조 스트림은 FilterInputStream이나 FilterOutputStream을 상속 받는다.
- 이들 클래스를 상속받은 보조 클래스도 상위 클래스에 디폴트 생성자가 없어므로 다른 스트림을 매개변수로 받아 상위 클래스를 호출해야 한다.
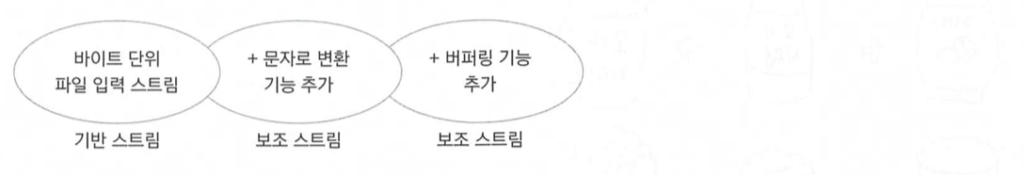
- 다른 보조 스트림을 매개변수로 전달 받을 수도 있다.
- 문자를 위해서 Reader나 Writer에서 상속 받은 스트림을 사용해 자료를 읽거나 써야 한다. 하지만 바이트 자료만 입력되는 스트림도 있다. (System.in)
- 또한 네트워크에서 소켓이나 인터넷이 연결되었을 때 읽거나 쓰는 스트림은 바이트 단위인 InputStream과 OutputStream이다.
- 이런 바이트 스트림을 문자로 변환해 주는 보조 스트림이 이 두 스트림이다.
- InputStreamReader 생성자
InputStreamReader(InputStream in)InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs)InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecorder dec)InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) : UTF-8, UTF-16
- charset을 지정하지 않으면 시스템 기본 charset이 지정된다.
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("reader.txt"));
try (isr) {
int i;
while ((i = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 이러면 바이트 단위 스트림에서 문자를 읽어올 수 있다.
- 표준 입출력 스트림 System.in과 .out은 모두 바이트 스트림이다. 특히 System.in은 콘솔 화면에서 한글을 읽을려면 InputStreamReader를 사용해야 한다.
- Scanner클래스는 이런 변환이 필요없다.
Buffered 스트림
- 이미 생성된 스트림에 배열 기능을 추가해 더 빠르게 입출력을 실행할 수 있는 버퍼링 기능을 제공한다.
BufferedInputStream : 바이트 단위로 읽는 스트림에 버퍼링 기능을 제공한다.BufferesOutputStream : 바이트 단위로 출력하는 스트림에 버퍼링 기능을 제공한다.BufferedReader : 문자 단위로 읽는 스트림에 버퍼링 기능을 제공한다.BufferedWriter : 문자 단위로 출력하는 스트림에 버퍼링 기능을 제공한다.- Buffered 스트림은 맴버 변수로 8192바이트 배열을 가지고 있다.
- 한번 자료를 읽을때 8KB를 한번에 읽고 쓸 수 있어 1바이트씩 작업할때 보다 훨씬 빠르다.
- 배열의 크기 역시 지정할 수 있다.
- 비교 예제 코드
public class FileCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
long mills = 0;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("origin.zip");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.zip");
try (fis; fos) {
mills = System.currentTimeMillis();
int i;
while ((i = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(i);
}
mills = System.currentTimeMillis() - mills;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(mills + "");
}
}
- 약 8MB 파일을 복사하는데 20151ms가 소요됐다 (느리다)
- 아래는 BufferedInputStream을 활용한 개선 코드
public class BufferedStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
long mills = 0;
BufferedInputStream bis =
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("origin.zip"));
BufferedOutputStream bos =
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("copy.zip"));
try (bis; bos) {
mills = System.currentTimeMillis();
int i;
while ((i = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(i);
}
mills = System.currentTimeMillis() - mills;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(mills + "");
}
}
- 실행결과 200ms정도로 엄청나게 빠른것을 알 수 있다.
- 바이트나 문자가 아닌 메모리 저장된 상태를 그대로 읽거나 쓰는 보조 스트림이다.
DataInputStream(InputStream in)DataOutputStream(OutputStream out)- 파일에 여러 자료형 값을 저장하고 불러오는 예제
public class DataStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data.txt");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
try (fos; dos) {
dos.writeByte(100);
dos.writeChar('A');
dos.writeInt(10);
dos.writeFloat(3.14f);
dos.writeUTF("뷁");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
try (fis; dis) {
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Decorator pattern
- 자바IO스트림은 데코레이터 패턴이다.
- 데코레이터 패턴에서는 클래스는 실제로 입출력이 가능한 클래스와 그렇지 않은 클래스로 구분된다.
- 기능이 동적으로 추가되는 클래스를 데코레이터라고 한다.
- 보조스트림은 자료형만 맞는다면 다른 보조스트림에 기능을 더해줄 수 있다
WhippedCreamCoffee whippedCreamCoffee = new WhippedCreamCoffee(new MocaCoffee(new LatteCoffee(new KenyaCoffee())));




